vue-router剖析 什么是路由 路由最开始出现在后端。以前用模版开发时或者老系统开发或者做php开发时经常会看到这种url
1 http://wwww.aaaa.edu.cn/bbs/forum.php
有时还会有带.asp或.html的路径,这就是所谓的SSR(Server Side Render),通过服务端渲染,直接返回页面。
服务端渲染(SSR)
其响应过程为:
2.服务器监听到80端口(或443)有请求过来,并解析url路径
3.根据服务器的路由配置,返回相应信息(可以是 html 字串,也可以是 json 数据,图片等)
4.浏览器根据数据包的Content-Type来决定如何解析数据
前端路由的诞生:
Ajax,全称 Asynchronous JavaScript And XML,是浏览器用来实现异步加载的一种技术方案。在 90s 年代初,大多数的网页都是通过直接返回 HTML 的,用户的每次更新操作都需要重新刷新页面。及其影响交互体验,随着网络的发展,迫切需要一种方案来改善这种情况。Knockoutjs 实现。但这项技术的强大之处并未当时的开发者体会到,可能是因为 Knockoutjs 实现过于复杂,导致没有大面积的扩散。
前端路由原理 对于vue-router和react-router等前端路由来看,其实原理很简单
url每次变化都会刷新页面吗?
页面刷新,javascript怎么检测和获取url?
对于这2个问题,在很早之前,开发者就想到解决办法:通过hash来实现路由
1 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011956628#articleHeader2
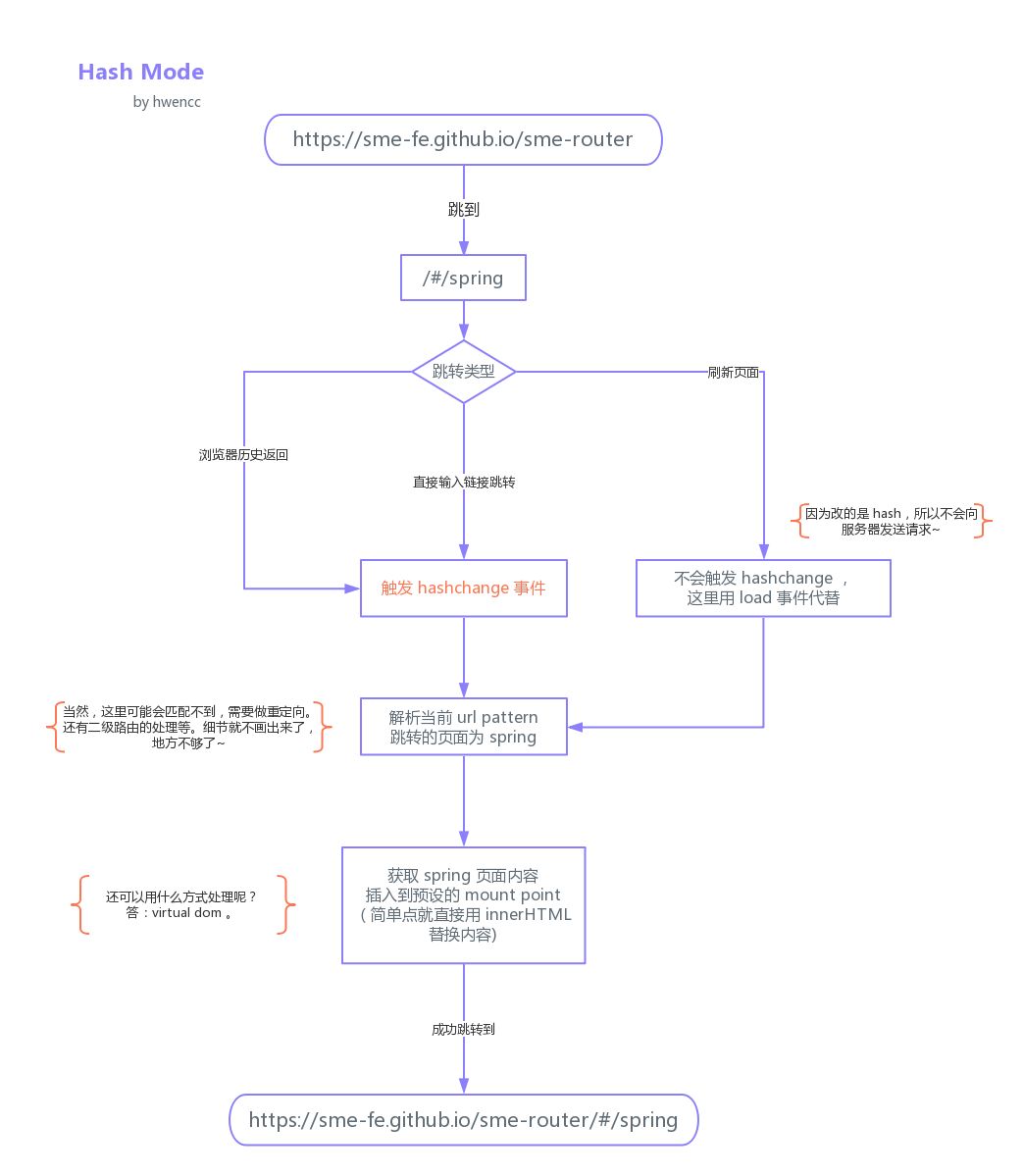
hash模式 这种 #。后面 hash 值的变化,并不会导致浏览器向服务器发出请求,浏览器不发出请求,也就不会刷新页面。另外每次 hash 值的变化,还会触发 hashchange 这个事件,通过这个事件我们就可以知道 hash 值发生了哪些变化.
对于hash模式实现路由流程如下:
hash实现方式不需要服务器的支持
而对于vue-router来说
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 setupListeners () { if (this .listeners .length > 0 ) { return } const router = this .router const expectScroll = router.options .scrollBehavior const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll if (supportsScroll) { this .listeners .push (setupScroll ()) } const handleRoutingEvent = ( const current = this .current if (!ensureSlash ()) { return } this .transitionTo (getHash (), route => if (supportsScroll) { handleScroll (this .router , route, current, true ) } if (!supportsPushState) { replaceHash (route.fullPath ) } }) } const eventType = supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange' window .addEventListener ( eventType, handleRoutingEvent ) this .listeners .push (() => { window .removeEventListener (eventType, handleRoutingEvent) }) }
检测到hash发生变化后通过替换dom形式来实现页面变换
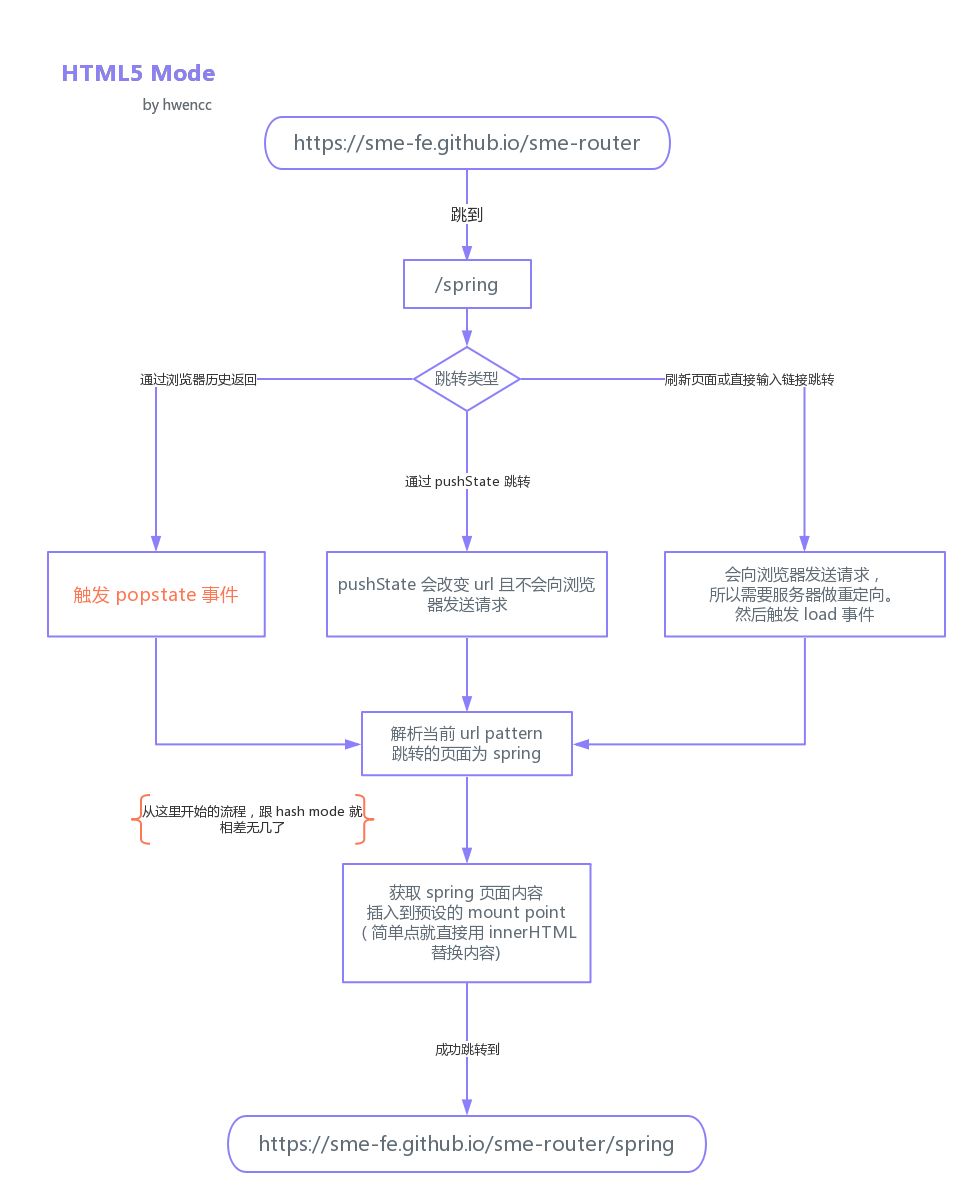
history模式 当html5发布后针对与url对象,新增了pushState, 和 replaceStateonpopstate 事件。通过这些就能用另一种方式来实现前端路由了,但原理都是跟 hash 实现相同的。用了 HTML5 的实现,单页路由的 url 就不会多出一个#,变得更加美观。但因为没有 # 号,所以当用户刷新页面之类的操作时,浏览器还是会给服务器发送请求。为了避免出现这种情况,所以这个实现需要服务器的支持,需要把所有路由都重定向到根页面。具体可以见:[HTML5 histroy 模式](HTML5 History 模式 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 export class HTML5History extends History { _startLocation : string constructor (router: Router, base: ?string ) { super (router, base) this ._startLocation = getLocation (this .base ) } setupListeners () { if (this .listeners .length > 0 ) { return } const router = this .router const expectScroll = router.options .scrollBehavior const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll if (supportsScroll) { this .listeners .push (setupScroll ()) } const handleRoutingEvent = ( const current = this .current const location = getLocation (this .base ) if (this .current === START && location === this ._startLocation ) { return } this .transitionTo (location, route => if (supportsScroll) { handleScroll (router, route, current, true ) } }) } window .addEventListener ('popstate' , handleRoutingEvent) this .listeners .push (() => { window .removeEventListener ('popstate' , handleRoutingEvent) }) } go (n : number) { window .history .go (n) } push (location : RawLocation , onComplete?: Function , onAbort?: Function ) { const { current : fromRoute } = this this .transitionTo (location, route => pushState (cleanPath (this .base + route.fullPath )) handleScroll (this .router , route, fromRoute, false ) onComplete && onComplete (route) }, onAbort) } replace (location : RawLocation , onComplete?: Function , onAbort?: Function ) { const { current : fromRoute } = this this .transitionTo (location, route => replaceState (cleanPath (this .base + route.fullPath )) handleScroll (this .router , route, fromRoute, false ) onComplete && onComplete (route) }, onAbort) } ensureURL (push?: boolean) { if (getLocation (this .base ) !== this .current .fullPath ) { const current = cleanPath (this .base + this .current .fullPath ) push ? pushState (current) : replaceState (current) } } getCurrentLocation (): string { return getLocation (this .base ) } } export function getLocation (base: string ): string { let path = window .location .pathname const pathLowerCase = path.toLowerCase () const baseLowerCase = base.toLowerCase () if (base && ((pathLowerCase === baseLowerCase) || (pathLowerCase.indexOf (cleanPath (baseLowerCase + '/' )) === 0 ))) { path = path.slice (base.length ) } return (path || '/' ) + window .location .search + window .location .hash }
对于vue-router来说上面的两种模式其实是依赖与浏览器环境。而对于实际开发过程中,往往出现另外一种情况:
abstract模式 abstract模式是使用一个不依赖于浏览器的浏览历史虚拟管理后端。支持所有 JavaScript 运行环境,如 Node.js 服务器端。
对于abstract根据平台差异可以看出,在 Weex 环境中只支持使用 abstract 模式。 不过,vue-router 自身会对环境做校验,如果发现没有浏览器的 API,vue-router 会自动强制进入 abstract 模式,所以 在使用 vue-router 时只要不写 mode 配置即可,默认会在浏览器环境中使用 hash 模式,在移动端原生环境中使用 abstract 模式。 (当然,你也可以明确指定在所有情况下都使用 abstract 模式)
而对于vue-router中abstract.js 中AbstractHistory是个比较特别的实现,因为它不是浏览器环境,所以它没有window.history,它不需要再去考虑popstate hashchange事件,不需要去管浏览器的地址栏,但是它需要自己管理路由历史记录。所在AbstractHistory里面,设置了stack数组来存储访问的路由对象,设置了一个index实例属性,来表示当前访问的路由位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 import type Router from '../index' import { History } from './base' import { NavigationFailureType , isNavigationFailure } from '../util/errors' export class AbstractHistory extends History { index : number stack : Array <Route > constructor (router: Router, base: ?string ) { super (router, base) this .stack = [] this .index = -1 } push (location : RawLocation , onComplete?: Function , onAbort?: Function ) { this .transitionTo ( location, route => this .stack = this .stack .slice (0 , this .index + 1 ).concat (route) this .index ++ onComplete && onComplete (route) }, onAbort ) } replace (location : RawLocation , onComplete?: Function , onAbort?: Function ) { this .transitionTo ( location, route => this .stack = this .stack .slice (0 , this .index ).concat (route) onComplete && onComplete (route) }, onAbort ) } go (n : number) { const targetIndex = this .index + n if (targetIndex < 0 || targetIndex >= this .stack .length ) { return } const route = this .stack [targetIndex] this .confirmTransition ( route, () => { const prev = this .current this .index = targetIndex this .updateRoute (route) this .router .afterHooks .forEach (hook => hook && hook (route, prev) }) }, err => if (isNavigationFailure (err, NavigationFailureType .duplicated )) { this .index = targetIndex } } ) } getCurrentLocation () { const current = this .stack [this .stack .length - 1 ] return current ? current.fullPath : '/' } ensureURL () { } }
go的处理 不同于Html5History HashHistory可以直接使用window.history.go来实现go这个方法,AbstractHistory必须自己来实现go方法。不过看go的代码,不太明白一点:为什么不直接用transitionTo这个统一的路由跳转入口,而是要使用更加底层的confirmTranstion方法。
这行代码:
1 2 3 if (isExtendedError (NavigationDuplicated , err)) { this .index = targetIndex }
找到这行代码的添加的原因了: bug fix 、issue
This PR provides a fix to the issue #2607.https://jsfiddle.net/Rocka/bhu5vkn8/3/
go里面的处理有一点是对的,就是不改变stack数组的内容,只调整访问的指针index。这是与浏览器历史记录管理的特点相符的.
replace处理 replace方法看起来对于历史记录的管理,跟浏览器的管理方式不同,就是它会删除掉当前记录之后的记录,而不是仅仅替换当前记录,这一点在注释中有说明。